What Happens to assets if an Estate isn't Probated in Oregon?
Probate is just the court administered transfer of property after their death. Not all property is subject to the court process and sometimes it doesn't make sense to initiate a probate proceeding.
Non-Probate Property
Beneficiary Designations
Some property doesn't have to be admitted to probate in order to transfer. Think about your bank, brokerage or life insurance accounts. Often times these accounts are transferable by the beneficiary designations. When you initially opened these accounts you were probably asked to select a beneficiary. Because these accounts are contracts between you and the bank, brokerage or insurance company, the beneficiary designation will direct whoever holds your account to transfer it to your beneficiary after your death.
Below is a snip from the Servicemember Group Life Insurance application.
If you read the language carefully it says "If you do not specifically name beneficiaries, your insurance will be paid by law." What this often means is that if you don't designate a beneficiary the accounts will be paid to the estate and administered by the court.
While this is a quick and inexpensive way to transfer property after death it is very limited. Like the picture above, most companies will allow you only a few options on how you want to distribute the account. If you want to split the proceeds in a more complicated way you will need a more involved estate planning.
Keeping Beneficiary Designations up to Date
Using a beneficiary designation is only helpful if it is accurate. I suggest that you review your accounts annually to make sure the designations are accurate and up to date. It's not uncommon to find former husbands and wives as beneficiaries on accounts years after a divorce. That is not a situation anyone wants to deal with your passing.
Transferable on Death Deeds
A few years Oregon adopted a Transfer on Death Deeds. I believe most states have adopted them at this point. Much like their name implies, these deeds transfer title in real estate on your death. TODD are one of the most loved estate planning tools if you have an uncomplicated family. The primary reason an estate has to be admitted to probate is real estate. Removing real estate from the equation may let you avoid probate or allow you to settle the estate via the Small Estate process.
I've inserted a snip from ORS 93.975 that provides the form for TODD deeds.
If you only have one heir then a Transfer on Death Deed may make sense for you but anything more complicated and I would be leery of using it.
Abandoning Property
Often times someone will die owing more money than their estate is worth. When this happens, heirs sometimes decide to just walk away and let the banks foreclose on the property.
If you have any questions about how probate works or what property is included, please feel free to contact me.
Oregon Probate Jurisdiction
One of the areas that initially confuses many practitioners is the limits of jurisdiction for Oregon Probate Courts. By and large, the jurisdiction of the probate court is the same as that of the Circuit Courts. ORS 111.075 Probate Jurisdiction Vested states:
Jurisdiction of all probate matters, causes and proceedings is vested in the county courts of Gilliam, Grant, Harney, Malheur, Sherman and Wheeler Counties and in the circuit court for each other county and as provided in ORS 111.115 (Transfer of estate proceeding from county court to circuit court).
The individual county courts that are vested with probate jurisdiction are the large sparsely populated counties of Eastern Oregon including the recently famous Harney County. Although the code says these six counties are vested with the county court, all of Oregon's 36 counties' has a circuit court. I don't know why this is.
ORS 111.085 Probate jurisdiction described:
The jurisdiction of the probate court includes, but is not limited to:
(1)Appointment and qualification of personal representatives.
(2)Probate and contest of wills.
(3)Determination of heirship.
(4)Determination of title to and rights in property claimed by or against personal representatives, guardians and conservators.
(5)Administration, settlement and distribution of estates of decedents.
(6)Construction of wills, whether incident to the administration or distribution of an estate or as a separate proceeding.
(7)Guardianships and conservatorships, including the appointment and qualification of guardians and conservators and the administration, settlement and closing of guardianships and conservatorships.
(8)Supervision and disciplining of personal representatives, guardians and conservators.
(9)Appointment of a successor testamentary trustee where the vacancy occurs prior to, or during the pendency of, the probate proceeding. [1969 c.591 §5; 1973 c.177 §1]
Now that we have a general description of the kinds of matters that the probate court is interested in, what are the limits of the court's powers. A phrase you might hear is that the circuit court is "sitting in probate." ORS 11.095(1) describes those powers:
The general legal and equitable powers of a circuit court are applicable to effectuate the jurisdiction of a probate court, punish contempts and carry out its determinations, orders and judgments as a court of record with general jurisdiction, and the same validity, finality and presumption of regularity shall be accorded to its determinations, orders and judgments, including determinations of its own jurisdiction, as to those of a court of record with general jurisdiction.
What does this all mean? In essence, the probate court is the circuit court. There exist some different procedural rules that expedite the administration of the estate in uncontested proceedings but for the most part the powers of the two are the same.
Intestate Succession in Oregon
What happens when you die without a will
When a person dies without a Will in place, the Oregon Probate Law (Intestate Succession and Wills) determines how that person’s estate will be distributed. The diagrams below will help you understand how the estate will be divided. This is not a complete list of scenarios but should give you a good idea of what can happen. In real life, families can be incredibly complicated and who inherits what can be equally as complicated.
Surviving Spouse and Children
No Surviving Spouse and Surving Children
When there is no surviving spouse, the Estate is distributed evenly between the children.
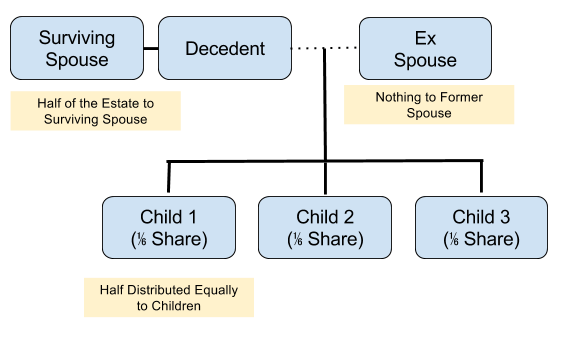
Children from a Previous relationship and a surviving spouse
In this situation, the surviving spouse receives half of the estate while the Decedent’s children receive the other half distributed evenly. Former spouse receives nothing.
Parents Share when Decedent has no children or spouse
When a Decedent passes with no Spouse or Children, the surviving Parent will inherit the estate.
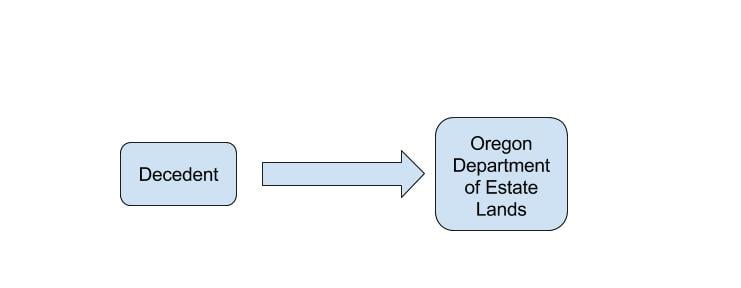
No Heirs, unable to locate heirs or heirs refuse
Caveats
There are many other situations that can arise with families. For example, parents can sometimes forfeit their share of estate because of neglect or abuse. If the heir murdered or abused the person who died, Oregon law can prevent them from inheriting property. There are also rules for grandparents inheriting property and for individuals inheriting property to two lines of relationships.
What appears first as simple can quickly become complicated when blended families, remarriages, not remarrying and other decisions we make throughout life get added to the mix.You can learn more about Oregon Probate on my practice area page.
If you have any questions on how your property will be inherited after you pass, feel free to contact me.
Search the blog and learn more about wills and probate in Oregon.
Disclaimer:
Nothing on this blog constitutes individual legal advice or creates an Attorney-Client relationship.
-
May 2023
- May 8, 2023 What is a Limited Judgment Appointing Personal Representative? May 8, 2023
- May 1, 2023 Where should I keep estate planning documents? May 1, 2023
-
April 2023
- Apr 24, 2023 How do I talk to my elderly parents about estate planning? Apr 24, 2023
- Apr 17, 2023 How do I get started in estate planning? Apr 17, 2023
- Apr 10, 2023 What questions should I ask my estate planning attorney? Apr 10, 2023
- Apr 5, 2023 Giving Appreciated Property to Charity in Oregon Apr 5, 2023
- Apr 3, 2023 How often should an estate plan or will be updated or reviewed? Apr 3, 2023
-
March 2023
- Mar 30, 2023 Is real property located outside of Oregon subject to the Oregon estate tax? Mar 30, 2023
- Mar 29, 2023 How do I find out who the personal representative of an estate is? Mar 29, 2023
- Mar 27, 2023 Why is estate planning so expensive? Mar 27, 2023
- Mar 23, 2023 Can non-residents be subject to the Oregon Estate Tax? Mar 23, 2023
- Mar 22, 2023 How do I sue a personal representative? Mar 22, 2023
- Mar 20, 2023 What are some estate planning steps that can ease financial burdens following the death of a loved one? Mar 20, 2023
- Mar 16, 2023 What is a credit shelter trust? Mar 16, 2023
- Mar 15, 2023 Who is the personal representative of an intestate estate? Mar 15, 2023
- Mar 13, 2023 How does a probate or personal representative bond work? Mar 13, 2023
- Mar 9, 2023 Does Oregon have a gift tax? Mar 9, 2023
- Mar 8, 2023 How can I leave money to my son but not his wife? Mar 8, 2023
- Mar 6, 2023 What is a power of attorney? Mar 6, 2023
- Mar 2, 2023 What is the importance of a schedule K-1 for an estate? Mar 2, 2023
- Mar 1, 2023 Overview of the Oregon Estate Tax Mar 1, 2023
- Mar 1, 2023 Oregon Estate Tax and the Fractional Formula Mar 1, 2023
- Mar 1, 2023 Can My Mother Leave Me Out of Her Will? Mar 1, 2023
-
February 2023
- Feb 27, 2023 What is a pour-over will? Feb 27, 2023
- Feb 24, 2023 How to remove squatters from a deceased person's home. Feb 24, 2023
- Feb 20, 2023 How can a revocable trust avoid a conservatorship? Feb 20, 2023
- Feb 17, 2023 A dead person owes me money, how do I file a claim? Feb 17, 2023
- Feb 16, 2023 What are the Oregon inheritance or succession laws? Feb 16, 2023
- Feb 13, 2023 What is a "revocable trust" or "living trust"? Feb 13, 2023
- Feb 6, 2023 Can property be transferred without probate? Feb 6, 2023
-
January 2023
- Jan 30, 2023 What happens to a bank account when someone dies without a beneficiary? Jan 30, 2023
- Jan 23, 2023 What is a Payable on Death bank account? Jan 23, 2023
- Jan 17, 2023 What happens if I don’t go through probate? Jan 17, 2023
- Jan 9, 2023 Does Oregon have a Transfer on Death deed? Jan 9, 2023
- Jan 2, 2023 What Triggers Probate in Oregon? Jan 2, 2023
- Jan 1, 2023 What is the 65 day rule for estates and trusts? Jan 1, 2023
-
May 2022
- May 10, 2022 Can a Will Avoid Probate? May 10, 2022
-
April 2022
- Apr 25, 2022 How Do You Avoid Probate in Oregon? Apr 25, 2022
- Apr 7, 2022 Must an Estate Go Through Probate in Oregon? Apr 7, 2022
-
March 2022
- Mar 28, 2022 How much does an estate have to be worth to go to probate in Oregon? Mar 28, 2022
-
September 2021
- Sep 3, 2021 We are closed for Labor Day. Sep 3, 2021
- Sep 2, 2021 How Long Does Probate Take in Oregon? (Updated for COVID) Sep 2, 2021
- Sep 2, 2021 How does probate work without a will in Oregon. Sep 2, 2021
-
January 2018
- Jan 18, 2018 2018 Oregon Estate Tax Rates Jan 18, 2018
- Jan 18, 2018 Is a Handwritten Will Valid in Oregon? Jan 18, 2018
-
December 2017
- Dec 18, 2017 Oregon Probate Fees in 2017 Dec 18, 2017
-
August 2017
- Aug 2, 2017 2017 Oregon Estate Tax Rates Aug 2, 2017
-
March 2017
- Mar 9, 2017 Oregon Probate Inventory Mar 9, 2017
-
November 2016
- Nov 26, 2016 Basics of an Oregon Estate Plan (Part 3) Nov 26, 2016
- Nov 8, 2016 Basics of an Oregon Estate Plan (Part 2) Nov 8, 2016
- Nov 1, 2016 Basics of an Oregon Estate Plan (Part 1) Nov 1, 2016
-
October 2016
- Oct 24, 2016 Duties of an Oregon Personal Representative Oct 24, 2016
-
September 2016
- Sep 6, 2016 Oregon Estate Planning Timeline Sep 6, 2016
-
June 2016
- Jun 23, 2016 How Long Does Probate Take in Oregon? Jun 23, 2016
- Jun 20, 2016 How to File for Probate in Oregon Jun 20, 2016
-
May 2016
- May 17, 2016 When is Probate required in Oregon? May 17, 2016
- May 6, 2016 Oregon Probate Bond May 6, 2016
- May 5, 2016 Oregon Personal Representative Checklist May 5, 2016
- May 3, 2016 Compensation of Personal Representative in Oregon May 3, 2016
-
April 2016
- Apr 29, 2016 2016 Oregon Estate Tax Rates Apr 29, 2016
- Apr 25, 2016 Probating Joint Bank Accounts in Oregon Apr 25, 2016
- Apr 19, 2016 How much does Probate cost in Oregon? Apr 19, 2016
-
March 2016
- Mar 3, 2016 What is a Guardianship in Oregon? Mar 3, 2016
-
February 2016
- Feb 26, 2016 Elements of an Oregon Estate Plan Feb 26, 2016
- Feb 24, 2016 Faith Based Estate Planning in Oregon Feb 24, 2016
- Feb 23, 2016 March Events Feb 23, 2016
- Feb 16, 2016 Self-Made Rich are more Generous Feb 16, 2016
- Feb 10, 2016 What Happens to assets if an Estate isn't Probated in Oregon? Feb 10, 2016
- Feb 8, 2016 Oregon Probate Jurisdiction Feb 8, 2016
- Feb 5, 2016 Do You Really Want to Die Rich? Feb 5, 2016
- Feb 4, 2016 2016 Oregon Legislation to watch Feb 4, 2016
- Feb 2, 2016 Probate Pitfalls (Investing Estate Assets) Feb 2, 2016
-
January 2016
- Jan 14, 2016 Intestate Succession in Oregon Jan 14, 2016
- Jan 13, 2016 Estate Planning for Unmarried Seniors Jan 13, 2016
- Jan 12, 2016 What does an Oregon Probate Attorney do? Jan 12, 2016
-
December 2015
- Dec 31, 2015 End of Life Decision Making in Oregon Dec 31, 2015
- Dec 21, 2015 Free Oregon Estate Planning Workshop Dec 21, 2015
- Dec 17, 2015 Non-borrowing surviving spouse can retain home subject to Reverse mortgage Dec 17, 2015
- Dec 3, 2015 Estate Planning for Digital Assets Dec 3, 2015
-
October 2015
- Oct 29, 2015 2015 Budget Deal putting an end to "File-and-Suspend" Social Security strategy Oct 29, 2015
- Oct 21, 2015 End of Year Estate Planning Oct 21, 2015
- Oct 12, 2015 Disinheriting Parents in Oregon Oct 12, 2015
- Oct 1, 2015 Inheriting Property when there is no Will. Oct 1, 2015
-
September 2015
- Sep 29, 2015 Negative Wills in Oregon Sep 29, 2015
- Sep 25, 2015 2016 Oregon Probate Law Modernization Sep 25, 2015
- Sep 21, 2015 The Probate Process in Oregon Sep 21, 2015
- Sep 15, 2015 2015 Oregon Estate Tax Rates Sep 15, 2015